Research Activities
Research Activities
Publications
November 04, 2014
Human iPSC-derived cell sheets with defined cardiovascular populations efficiently recover heart failure in rat
Promising preliminary results in cardiac cell therapy for heart failure has sparked hope to both researchers and patients in search of options beyond heart transplantation. Most important to the outcome of cardiac cell therapy is the functional restoration and engraft rate of the introduced cells, which depends on the cell type and cell delivery. Because they have unlimited proliferation potential and are able to differentiate into all cardiac cells, human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are regarded as a very attractive cell type. At the same time, the cell-sheet method is currently the most effective heart delivery method, because of its relatively high engraftment rate, although much improvement is needed.
One issue compromising the quality of a cell sheet is the constituency of its cells. Previous studies have made sheets exclusively of cardiomyocytes with encouraging but nevertheless disappointing results. A population that includes cardiomyoctyes and also endothelial and mural cells appears to significantly improve the generation of viable cell sheets, but generating such a heterogeneous population from hiPSCs has proven to be a challenge. The Jun Yamashita team now reports a method that differentiates hiPSCs into different cell types. Mixing the cell types resulted in the synthesis of cell sheets that when transplanted into a myocardial infarction rat model showed high graft survival and positive effects in the heart.
This work grew from the lab's previous study that used mouse embryonic stem cells. In the current work, they changed the culture conditions such that VEGF, an angiogenic cytokine, was included. "We had a method to exclusively induce cardiomyocytes from mesoderm precursors. For the new approach, we needed vascular cells from mesoderm in addition to cardiomyocytes," says Professor Yamashita. Consequently, hiPSCs were differentiated into a heterogeneous population, although more than 75% constituted cardiomyoctyes (see image).
Transplantation of the sheets into rat caused significant improvement in a number of cardiac parameters including left ventricle systolic function, fractional shortening and systolic thickening among others, indicating that remodeling of the left ventricle, a common outcome of myocardial infarction, was suppressed.
Although a number of studies have reported the benefits of cardiac stem cell therapy, there is still much question whether the observed benefits are directly due to the graft or whether they are the result of paracrine effects from growth factors secreted by the engrafted cells. "At this state, we can say cellular interactions increased the secretion of growth factors, including angiogenic factors." Clarifying the optimal proportion of different cell types will be crucial for efficient and long-term survival of the grafts in the treatment of heart failure.
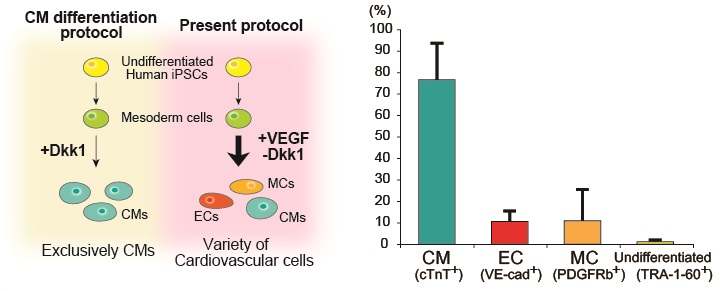
(left) In the original protocol, hiPSCs were differentiated exclusively into cardiomyocytes. In the present protocol, Dkk1 was replaced with VEGF in the culture, which resulted in a heterogeneous population of cardiovascular cells. (right) Cardiomyocytes still constituted the vast majority of the population, however. CM, cardiomyoctyes; EC, endothelial cells; MC, mural cells.
Paper Details
- Journal: Scientific Reports
- Title: Human iPS cell-engineered cardiac tissue sheets with cardiomyocytes and vascular cells for cardiac regeneration
- Authors: Hideotoshi Masumoto, Takeshi Ikuno, Masafumi Fukushima, Akira Marui, Shiori Katayama, Tatsuya Shimizu, Tadashi Ikeda, Teruo Okano, Ryuzo Sakata, Jun K Yamashita