News & Events
News & Events
News
September 27, 2022
A new method for inducing mesenchymal stem cells from iPS cells without using animal-derived components
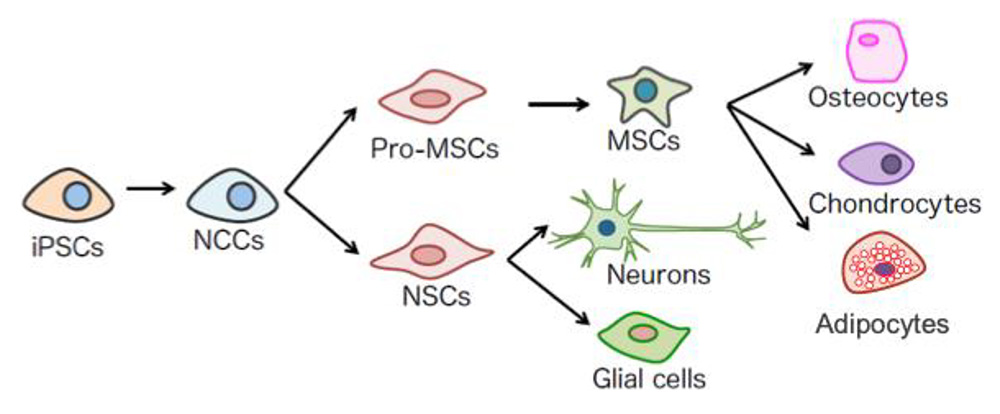
MSCs are stem cells that exist in the adult body and are being used for cell transplantation in regenerative medicine for various diseases. The Makoto Ikeya laboratory previously reported a method for inducing MSCs from iPS cells, but it was not suitable for use in cell transplantation therapy because the protocol involved animal-derived components.
The research group has established a new protocol to efficiently induce differentiation from iPS cells to MSCs under conditions that were free of animal-derived substances (XF: Xeno-Free). These MSCs (XF-iMSCs) were transplanted into mice. The researchers found that the XF-iMSCs were able to regenerate bone and skeletal muscle in the mice. The XF-iMSCs not only differentiated into bone cells but also secreted factors that promoted the regeneration of surrounding cells. These results suggest that XF-iMSCs have the potential to be used in regenerative medicine.
The results of this study were published online in npj Regenerative Medicine on September. 15, 2022.
Paper Details
- Journal: npj Regenerative Medicine
- Title: Induction of functional xeno-free MSCs from human iPSCs via a neural crest cell lineage
- Authors:
Daisuke Kamiya1,4, Nana Takenaka-Ninagawa1, Souta Motoike1,2, Mikihito Kajiya2, Teppei Akaboshi1,4, Chengzhu Zhao1, Mitsuaki Shibata1, Sho Senda3, Yayoi Toyooka1,4, Hidetoshi Sakurai1, Hidemi Kurihara2, Makoto Ikeya1,4*
*:Corresponding authors - Author Affiliations:
- Dept. of Clinical Application, Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University, 53 Kawahara-cho, Shogoin, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8507, Japan
- Institute of Biomedical & Health Sciences, Graduate School of Biomedical & Health Sciences, Hiroshima University, 1-2-3, Kasumi, Minami-ku, Hiroshima 734-8553, Japan
- Research Institute for Bioscience Product & Fine Chemicals, Ajinomoto Co., Inc., Kawasaki, 210-8681, Japan
- Takeda-CiRA Joint program (T-CiRA), Fujisawa, Kanagawa, Japan