Research Activities
Research Activities
CiRA IP
Intellectual Property of CiRA
As of April 2025, Kyoto University holds basic patents related to iPS cell technology in the following countries and regions.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, India, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Liechtenstein, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Portugal, Russia, Singapore, Spain, South Africa, South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, the United States.
The scope of iPS cell-related patents owned by Kyoto University is described below. According to the provisions of the Patents Act and Law, such patents also cover cells produced through the manufacturing processes claimed in such patents. The term of the patents is 20 years beginning from December 6, 2006 as the international filing date of PCT patent application which is root application of those patents.
The patents are licensed through iPS Academia Japan, Inc.
- For the public › FAQ › What are iPS cells?CiRA IP
In Japan
| JP4183742 |
A method for preparing iPSC through the introduction of four reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc) into somatic cell. |
|---|---|
| JP4411362 |
A method for preparing iPSC through the introduction of three reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4) into somatic cell and the culturing in the presence of bFGF. |
| JP4411363 |
A method for preparing somatic cells, which comprise production process for the generation of iPSC generated either through the introduction of three reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4) into somatic cell and the culturing in the presence of bFGF, or through the introduction of four reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc) into somatic cell, and the generation of somatic cell from such iPSC through induced differentiation. |
| JP5098028 |
|
| JP5248371 |
|
| JP5467223 |
A method for producing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising the following (1) to (3) steps;
|
| JP5603282 |
A method for producing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising the following (1) to (3) steps;
|
| JP5943324 |
A method for producing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising the following (1) to (3) steps;
|
(*1) The term "specific gene families" stands for the set of gene families each of which is specifically identified as :
- - Oct family corresponds to Oct3/4
- - Klf family consists of Klf2 and Klf4
- - Myc family consists of c-Myc, N-Myc, L-Myc and T58A (mutational gene of c-Myc)
- - Sox family consists of Sox1, Sox2, Sox3, Sox15 and Sox17
Overseas
| US8,048,999 |
A reprogramming factor comprising genes of an Oct family, a Klf family, and a Myc family. |
|---|---|
| US8,058,065 |
A method for preparing iPSC through the introduction by retroviral vector(s) comprising four reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc) into somatic cell and the post culturing on a fibroblast feeder layer or an extracellular matrix with ES cell growth condition. |
| US8,129,187 |
A method for preparing mammalian somatic cell(s) by differentiating iPSC obtained through the use of four reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc) under substantially the same process of above US8,058,065 patent. |
| US8,278,104 |
A method for preparing iPSC by nuclear reprogramming of a mammmalian somatic cell, comprising the steps of introducing into the mammalian somatic cell one or more retroviral vectors comprising reprogramming genes (Oct3/4, Klf4, Sox2) , and culturing the transduced somatic cell in the presence of a cytokine. |
| EP1970446 |
A reprogramming factor comprising genes or gene products of an Oct family, a Klf family, and a Myc family. |
| EP2206778 |
An in vitro method for evaluating the physiological function, efficacy or toxicity of a compound, a medicament or poison on cells differentiated from iPSC in which ① Oct family genes, Klf family genes, Sox family genes, and Myc family genes were transduced and cultured cytokines. |
| EP2208786 |
An in vitro method for reprogramming a somatic cell which comprises contacting somatic cells with a nuclear reprograming factor comprising ① Oct family genes, Klf family genes, Sox family genes, and Myc family genes and cultures them with cytokines. |
- * Oct family includes several similar genes such as Oct3/4, Oct1A, Oct6.
- * Klf family includes several similar genes such as Klf4, Klf1, Klf5.
- * Myc family includes several similar genes such as c-Myc, L-Myc, N-Myc.
- * Cytokine includes proteins such as bFGF,SCF and LIF.
- * Factors such as Sox2 unmentioned in the claim are also included in the patent right even though they are used in reprogramming or not.
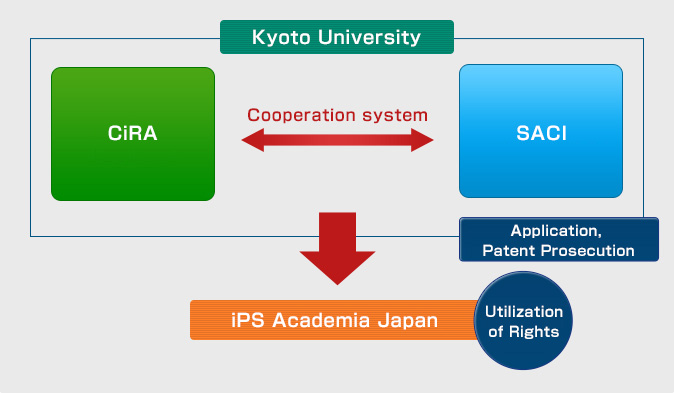
Intellectual property management system at Kyoto University
In order to manage iPS cell-related patents, CiRA is working together with the Kyoto University Office of Society Academia Collaboration for Innovation (SACI) and iPS Academia Japan.
iPS cells related intellectual property management system