Research Activities
Research Activities
Publications
March 04, 2022
Dissection of the polygenic architecture using iPSC lines derived from Alzheimer's disease
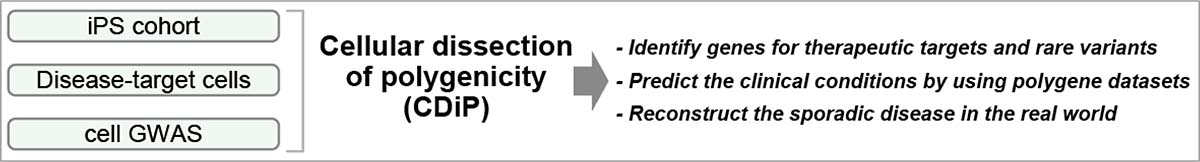
A research team led by CiRA Professor Haruhisa Inoue has developed a cellular dissection of polygenicity (CDiP) technology, which enables to reconstruct clinical conditions of Alzheimer's disease (AD) from patients' genetic data by using iPS cells and artificial intelligence.
First, the group used the "iPS Cohort," which consists of iPS cells generated from 102 patients with sporadic AD, and then the iPS cells were differentiated into cerebral cortex neurons. A genome-wide analysis on the neuronal production of amyloid β was conducted to understand the cellular polygenicity of sporadic AD by decomposing the complicated AD pathology into cell types and phenotypes, which show pathological traits.
The researchers revealed genetic loci as genetic risks, identified therapeutic targets and rare variants of AD, and succeeded in machine learning-based prediction of the clinical conditions by using the data of AD cohort studies (ADNI and J-ADNI). This research results, achieved by CDiP technology, are expected to contribute to prediction and avoidance of sporadic AD disease conditions.
The findings of the research were published online on February 18, 2022, in the British scientific journal Nature Aging.
Paper Details
- Journal: Nature Aging
- Title: Dissection of the polygenic architecture of neuronal Aβ production using a large sample of individual iPSC lines derived from Alzheimer's disease patients
- Authors:
Takayuki Kondo1,2,3, Norikazu Hara4, Satoshi Koyama5, Yuichiro Yada2,3, Kayoko Tsukita2,3, Ayako Nagahashi1,2, Takeshi Ikeuchi4, Kenji Ishii6, Takashi Asada7, Tetsuaki Arai7,
Ryo Yamada5, Japanese Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (J-ADNI), Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), Haruhisa Inoue1,2,3,8*
* Corresponding author - Author Affiliations:
- Medical-risk Avoidance based on iPS Cells Team, RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project (AIP), Kyoto, Japan
- Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- iPSC-based Drug Discovery and Development Team, RIKEN BioResource Research Center (BRC), Kyoto, Japan
- Department of Molecular Genetics, Brain Research Institute, Niigata University, Niigata, Japan
- Unit of Statistical Genetics, Center for Genomic Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
- Research Team for Neuroimaging, Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Gerontology, Tokyo, Japan
- Department of Psychiatry, Division of Clinical Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
- Institute for Advancement of Clinical and Translational Science (iACT), Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan